Jianpan Huang1, Joseph H. C. Lai1, Xiongqi Han1, Zilin Chen1, Yang Liu1, Peng Xiao1, Lin Chen2,3, Jiadi Xu2,3, and Kannie W. Y. Chan1,3,4
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Research Institute, Baltimore, MD, United States, 3Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 4City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen, China
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2F.M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Research Institute, Baltimore, MD, United States, 3Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 4City University of Hong Kong Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen, China
A sensitive dynamic glucose enhanced (DGE) MRI acquisition and post-processing scheme was proposed to detect glucose signals from the brain parenchyma and cerebrospinal fluid at a low concentration of D-glucose (12.5% w/w) injection.
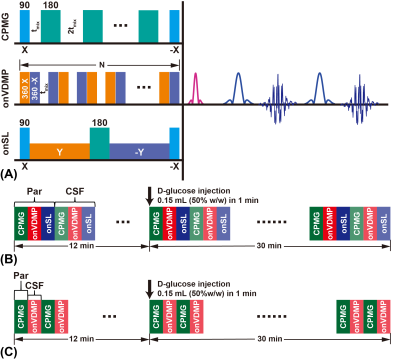
FIGURE 1. MRI sequences and protocols. (A) Three different saturation modules (CPMG, onVDMP, and onSL) followed by the same readout module (RARE). DGE MRI protocol that used in DGE experiments with 50% w/w (B) and 25%/12.5% w/w (C) D-glucose injection.
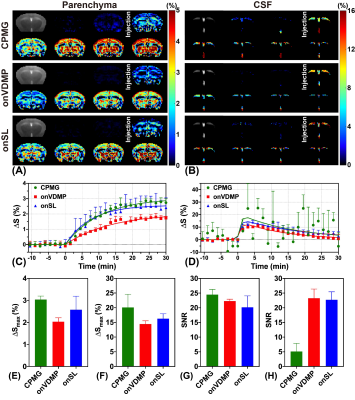
FIGURE 2. Comparison results of three DGE MRI methods with 50% D-glucose injection. Parenchyma (A) and CSF (B) DGE images acquired by CPMG, onVDMP and onSL. Parenchyma (C) and CSF (D) DGE curves acquired by CPMG, onVDMP and onSL. DGE images were averaged over sets of 4 for display (7 out of 28). Fitted ΔSmax of parenchyma (E) and CSF (F). SNR of parenchyma (G) and CSF (H).
