Romain Froidevaux1, Markus Weiger1, and Klaas Paul Pruessmann1
1Institute for Biomedical Engineering, ETH Zurich and University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
1Institute for Biomedical Engineering, ETH Zurich and University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
We demonstrate a method for algebraic reconstruction of ZTE
datasets with large central gaps, based on the knowledge of the excitation pulse.
It enables the use of longer pulses and overcomes flip angle limitations. Results
include phantom and in-vivo imaging.

Fig. 3: ZTE MRI of a water bottle using long RF
excitation pulses. In conventional ZTE, for gaps ≥ 4 dk, amplification of noise and aliased signal
create artifacts that dominate the images. However, PPE-ZTE preserves image
quality, even with long sweep pulses. The linear grey-scaling is normalized to
the maximum of each image separately.
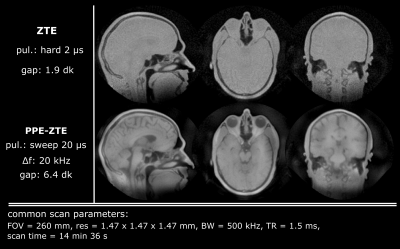
Fig. 5: In-vivo PPE-ZTE MRI in the head. ZTE is limited to proton-density
contrast due to the low flip angle reached with short block pulses, even at
maximum power. However, PPE-ZTE allows the use of longer sweep pulses that
create larger flip angles and consequently T1 contrast, in this case mostly
between the cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissues. Furthermore, short-T2 signal of the eye
lenses stands out against the vitreous body. Remaining low intensity variation are
likely to stem from residual model violations.