Ayse Sila Dokumaci1, Fraser R. Aitken1, Jan Sedlacik1, Philippa Bridgen1, Raphael Tomi-Tricot1,2, Tom Wilkinson1, Ronald Mooiweer1, Sharon Giles1, Joseph V. Hajnal1, Shaihan Malik1, Jonathan O'Muircheartaigh1, and David W. Carmichael1
1Division of Imaging Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Limited, Frimley, United Kingdom
1Division of Imaging Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Limited, Frimley, United Kingdom
A
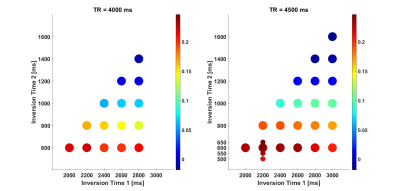
single acquisition obtaining FLAWS and UNI MP2RAGE images was optimised at
different repetition times using the EPG formalism accounting for B1+ variability
at 7T. Healthy subjects’ scans showed that UNI and FLAWS images could be
obtained together while largely maintaining image quality.
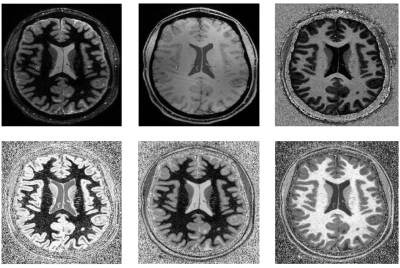
Figure 3. Transversal images from a representative
volunteer acquired with the shortest TR (4000ms). Top row (left to right) shows
the INV1 (suppressed WM), INV2 (suppressed CSF), and UNI images. Bottom row
(left to right) displays the FLAWSmin, FLAWShc, and FLAWShco
images. 240
slices were acquired with a slice partial Fourier of 6/8 and a GRAPPA factor of
3. FOV was 207mmx207mm. The scan duration was under 8.5 minutes. A 32-channel
TX/RX head coil was used.