Xi Chen1, Wenchuan Wu1, and Mark Chiew1
1Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, FMRIB, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
1Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, FMRIB, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
tSNR in 3D Multi-Shot EPI FMRI at 7T is improved by using a segmented CAIPI sampling trajectory and low-rank constrained reconstruction.
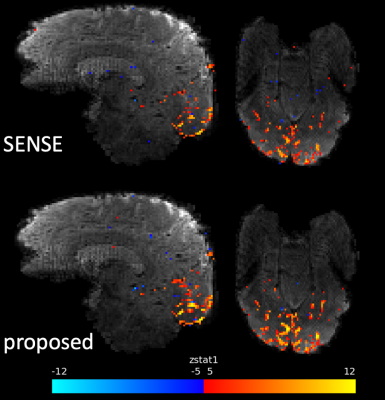
Figure 5. Activation maps resulting from the flashing checkerboard experiment by the shot-combined SENSE reconstruction (top) and the proposed reconstruction (bottom). In the sagittal view, activation in the calcarine sulcus is better characterised in the proposed reconstruction, and overall improved sensitivity to activation and higher peak z-stats are observed in the proposed reconstruction.
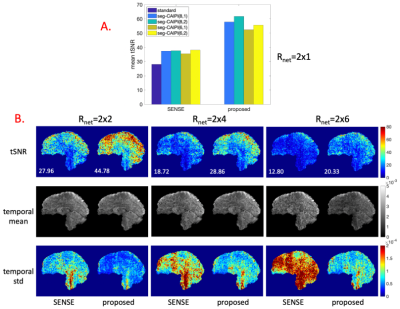
Figure 4. The reconstruction results of the 1.8mm in-vivo data. A. Mean tSNR across the whole brain for different trajectory choices by the conventional shot-combined SENSE reconstruction and the proposed reconstruction for the original Rnet=2x1 data without retrospective under-sampling. B. tSNR(mean value shown on the bottom left), temporal mean and standard deviation maps by the conventional shot-combined SENSE reconstruction(left) and the proposed reconstruction(right) for the seg-CAIPI(8,2) trajectory at Rnet=2x2, Rnet=2x4 and Rnet=2x6.
