Augix Guohua Xu1, Sunhang Shi1, Yunyun Rui1, Xiaotong Zhang1, Lizabeth Romanski2, Katalin M. Gothard3, and Anna Wang Roe1
1Interdisciplinary Institute of Neuroscience and Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2Dept of Neuroscience, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, NY, United States, 3University of Arizona, Dept of Physiology, Tucson, AZ, United States
1Interdisciplinary Institute of Neuroscience and Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2Dept of Neuroscience, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, NY, United States, 3University of Arizona, Dept of Physiology, Tucson, AZ, United States
We have previously shown that INS-fMRI is a rapid method for mapping mesoscale brain networks in the macaque monkey brain. Here, we extend this capability by stimulating deep brain sites.
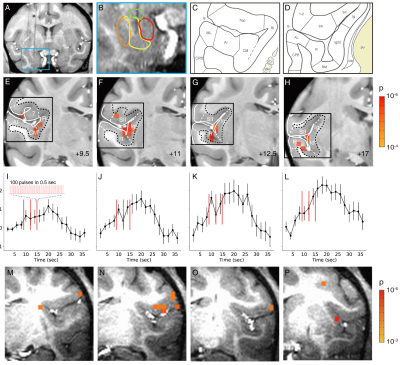
Figure 1. Activation in insula and lateral sulcal areas elicited by stimulation of the basal nucleus of the amygdala.
A-L. Monkey M-P. Monkey Y. A-B. Stimulation site in the basal nucleus. C-D. Schematics of cortical areas in the lateral sulcus. E-H. Activations within the lateral sulcus. Voxels: p<0.0001 (FDR 5.5%). I-L: Mean time courses of significant voxels in E-H (mean of significant voxels). Inset: enlarged schematic of each stimulus train (red line). Stimulation: block design. Error bars: SEM. M-P. Activations within the lateral sulcus are seen in monkey Y. Voxels: p<0.001.