Rita Gil1, Mafalda Valente1, Alfonso Renart1, and Noam Shemesh1
1Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal
1Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal
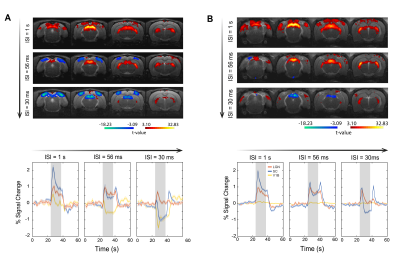
Our findings reveal attenuated SC negative BOLD responses (NBRs) at short inter-stimulus intervals upon V1 lesion and monocular stimulation highlighting the importance of corticotectal feedback and tectotectal projections in SC NBRs.
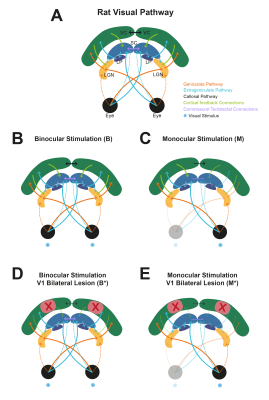
Fig.1: Stimulation Regimes (A) Rat visual pathway schematic. Orange - geniculate pathway; Blue - extrageniculate pathway; Black - Callosal pathway; Green: Cortical feedback projections; Light Purple: Commissural tectotectal projections. The blue dots represent the visual stimulus (either monocular or binocular). The different stimulation regimes and the implications along the pathway are represented in the different panels: (B) Binocular stimulation; (C) Monocular stimulation; (D) Binocular stimulation with V1 lesion; (E) Monocular stimulation with V1 lesion.