Parna Eshraghi Boroojeni1, Yasheng Chen2, Paul K. Commean1, Cihat Eldeniz1, Udayabhanu Jammalamadaka1, Gary B. Skolnick3, Kamlesh B. Patel3, and Hongyu An1
1Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis, Saint louis, MO, United States, 2Department of Neurology, Washington University in St. Louis, Saint louis, MO, United States, 3Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Washington University in St. Louis, Saint louis, MO, United States
1Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis, Saint louis, MO, United States, 2Department of Neurology, Washington University in St. Louis, Saint louis, MO, United States, 3Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Washington University in St. Louis, Saint louis, MO, United States
A deep learning-based method was developed to derive pseudo-CT from MR to provide cranial bone information for pediatric patients with head trauma and craniosynostosis without radiation exposure. The pCT closely resembles the gold standard CT images.
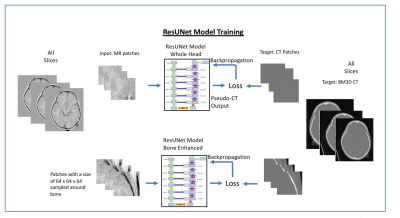
Fig 1 ResUNetModel training scheme. Two networks: whole head ResUNet and bone enhanced networks were trained. The patches were randomly selected from the whole head. For the bone enhanced network the placement of the patch is determined by the patches center voxels located within the bone.
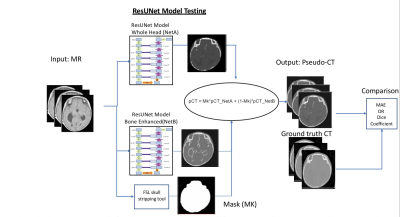
Fig 3 ResUNet Model testing scheme. The final pCT output was created by combining the pCT from the two networks. The whole head network pCT output was multiplied by brain mask and the bone enhanced network pCT output was multiplied by one minus the brain mask. The results of both multiplications were added for the final pCT output.