Suhyung Park1,2, Sugil Kim3, Hankyeol Lee4, Seulgi Eun4, Seong-Gi Kim4,5, and David Feinberg6,7
1Department of Computer Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of ICT Convergence System Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea, Republic of, 3Siemens-Healthineers, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 4Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (CNIR), Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Suwon, Korea, Republic of, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea, Republic of, 6University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States, 7Advanced MRI Technologies, Sebastopol, CA, United States
1Department of Computer Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of ICT Convergence System Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea, Republic of, 3Siemens-Healthineers, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 4Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (CNIR), Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Suwon, Korea, Republic of, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea, Republic of, 6University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States, 7Advanced MRI Technologies, Sebastopol, CA, United States
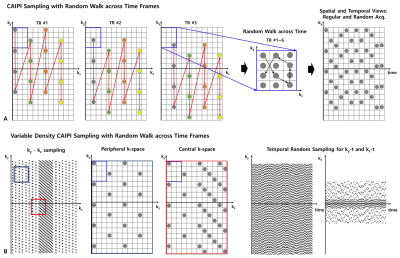
With ultra-high fields, 3D EPI has been used by improving imaging efficiency. We developed a novel accelerated 3D EPI using VD-CAPI sampling with temporal random walk. Experimental studies confirm advantages in acceleration, SNR, and sensitivity of the proposed method.
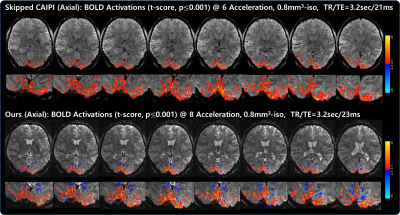
Fig. 3. Comparisons of visual activation maps (t-score, p≤0.001) overlaid on the average 3D EPI images observed from axial view: skipped CAIPI (top) vs.VD-CAIPI+Random Walk (bottom). Note that the proposed method yields higher BOLD activations in close proximity to gray matter compared to skipped CAIPI.