1Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main, Mainz, Germany, 2Faculty of Psychology and Neuroscience, Maastricht University, Maastricht, Netherlands, 3Scannexus, Maastricht, Netherlands, 4Brain Innovation, Maastricht, Netherlands, 5NIH, Bethesda, MD, United States
- We present an open dataset of whole brain layer-fMRI during movie watching.
- This data set is used to characterize the prospects and challenges of layer-fMRI.
- We discuss an atlas of intrinsic laminar profiles and layer-dependent vascular reactivity.
Finding best layer smoothing.
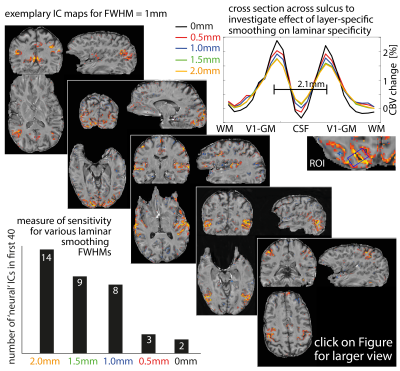
Since layer-fMRI is limited by SNR constraints, it can be hard to extract meaningful networks without spatial smoothing. Here we use ICA and take the nr. of ‘neural’ ICs as a proxy for sensitivity across smoothing strengths (bottom left). The distinguishability of two layer peaks (two GM banks in V1 2.1 mm apart) is used as a proxy for specificity (top right). These quality metrics are compared across laminar specific smoothing strengths.
Diagonals depicts representative ICA-derived connectivity maps.

Finding best layer smoothing.
Since layer-fMRI is limited by SNR constraints, it can be hard to extract meaningful networks without spatial smoothing. Here we use ICA and take the nr. of ‘neural’ ICs as a proxy for sensitivity across smoothing strengths (bottom left). The distinguishability of two layer peaks (two GM banks in V1 2.1 mm apart) is used as a proxy for specificity (top right). These quality metrics are compared across laminar specific smoothing strengths.
Diagonals depicts representative ICA-derived connectivity maps.
