1Dept. of Physics, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Centre for Medical Image Computing and Dept. of Computer Science, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Center for Biomedical Imaging, Dept. of Radiology, New York University, New York, NY, United States, 4CIBM Center for Biomedical Imaging, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
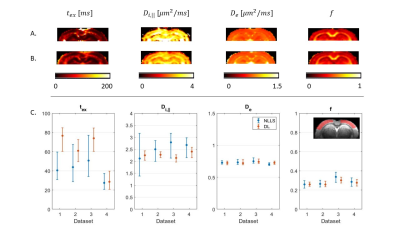
Fig.4: GRAMMI parametric maps calculated with NLLS (A) & DL (B) from a multi-shell multi-td dataset. The maps are overall homogeneous, with good differentiation between GM & WM. C: Median & IQR of model parameters in the cortex ROI across the 4 datasets. Experimental trends agree with the simulations. For De and f, NLLS and DL results are consistent, with better precision for DL Regarding tex the two methods agree very well for Dataset #4, which had the highest SNR (larger voxels), but the specific tex estimate may be biased due to only 3 diffusion times available instead of 4 (Fig. 1).
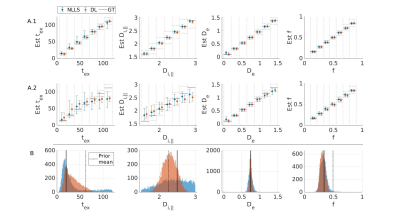
Fig.3: Simulation results fitting multi-shell multi-td data jointly for random (A) and fixed (B) GT. A: Displayed are the medians & IQR in each bin. Black lines: ideal estimation ±10 % error. Without noise (A1) DL and NLLS fit all parameters with high accuracy and precision. At SNR=100 (A2) some sensitivity to Di and high tex values is lost but still better than single td fits (Fig.2). DL has better precision than NLLS. B: At SNR=100, good accuracy is achived for tex, De and f with both NLLS and DL. For Di the precision is poor with NLLS while DL biases the outcome