Ileana O. Jelescu1,2 and Dmitry S. Novikov3
1CIBM Center for Biomedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Animal Imaging and Technology, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3Dept. of Radiology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
1CIBM Center for Biomedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Animal Imaging and Technology, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3Dept. of Radiology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
We examine the time-dependence and b-value
dependence of the Standard Model parameter estimates in the rat brain in vivo.
We show that exchange dominates and offer the picture of diffusion time
effectively filtering out the contribution of unmyelinated axons with stronger
dispersion.
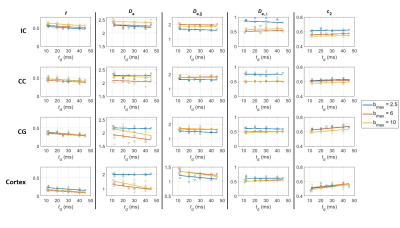
Fig. 4. SM parameter estimates (columns) in each ROI
(rows) as a function of td. Colors: bmax retained for the fit. Time-dependence is pronounced for f and c2 while
b-dependence is not. Conversely, for diffusivities, the b-dependence is
pronounced while the time-dependence is neither systematic nor consistent. Da decreases with time for all ROIs and bmax but most significantly in the cortex at bmax ≥ 6. Extra-axonal diffusivities
show a less systematic behavior with some trend for De,|| to decrease and
De,ꓕ
to increase, but none of them significant.
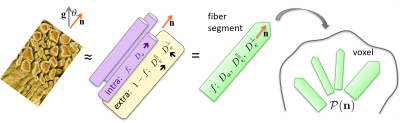
Fig.1:
Schematic of the SM of diffusion in WM, accounting for two
non-exchanging compartments: the intra-axonal space (with a relative weight f)
and the extra-axonal space. Da:
intra-axonal diffusivity, De,|| / De,ꓕ: extra-axonal axial / radial
diffusivities. These
unitary fascicles are distributed in the voxel given an orientation distribution
function P(n), for which the first few rotationally-invariant spherical harmonics
coefficients can be estimated – along with the 4 scalar parameters – by the
RotInv framework. [Image taken from Ref. 1].