Guillaume Frebourg1,2, Aurélien Massire1,2, Lauriane Pini1,2, Maxime Guye1,2, Bertrand Audoin2,3, Annie Veschueren2,4, Pierre-Hugues Roche5, and Virginie Callot1,2
1Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, CRMBM, Marseille, France, 2AP-HM, Hôpital de la Timone, CEMEREM, Marseille, France, 3AP-HM, Hôpital de la Timone, Neurology Dept., Marseille, France, 4AP-HM, Hôpital de la Timone, Neuromuscular Disease Dept., Marseille, France, 5AP-HM, Hôpital Nord, Neurosurgery Dept., Marseille, France
1Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, CRMBM, Marseille, France, 2AP-HM, Hôpital de la Timone, CEMEREM, Marseille, France, 3AP-HM, Hôpital de la Timone, Neurology Dept., Marseille, France, 4AP-HM, Hôpital de la Timone, Neuromuscular Disease Dept., Marseille, France, 5AP-HM, Hôpital Nord, Neurosurgery Dept., Marseille, France
A retrospective evaluation of SC image quality from 66 subjects was performed. MP2RAGE and DTI provided the best image quality, hence opening great perspectives for clinical or multi-centric transfer. New RF coils and pTx should help mitigating identified penalizing factors.
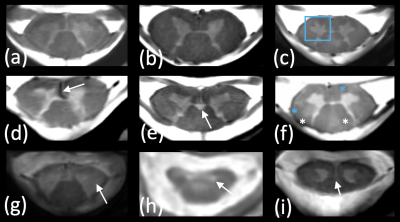
Fig.5 – 7T MRI offers new perspectives for SC characterization. Some atypical presentations, with details not seen on 3T scanners are presented here. (a, b) reference HC, (c) MS lesion in posterior funiculi with atypical ventral gray horn shape, (d) strong vascular hyposignal, (e) central canal dilatation, (f) MS patient presenting with several lesions (blue *not seen at 3T), (g) ALS patient presenting with strong degeneration of lateral funiculi, (h) MND patient presenting with strong hypersignal in GM (snake eyes), (i) MND patient with severe atrophy of the central GM commissure.
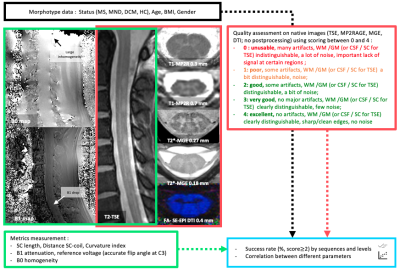
Fig. 1 – Anatomical and structural native image quality assessment of 4 MR sequences (TSE, MP2RAGE, MGE, DTI) along the whole volume or for each slice from C1 to C7, using scoring between 0 and 4. Average scores and success rate were calculated for each modality and cohort. Images with a score ≥ 2 were qualified as "GOOD” and considered for the success rate calculation. B1+ and B0 inhomogeneities were evaluated as well using relative variations in %. BMI: body mass index (kg/m2).
