Harkiran K Kooner1, Marrissa J McIntosh1, Maksym Sharma1, Alexander M Matheson1, Yasal Rajapaksa1, Inderdeep Dhaliwal2, Michael Nicholson2, and Grace Parraga1
1Robarts Research Institute, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Department of Medicine, Western University, London, ON, Canada
1Robarts Research Institute, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Department of Medicine, Western University, London, ON, Canada
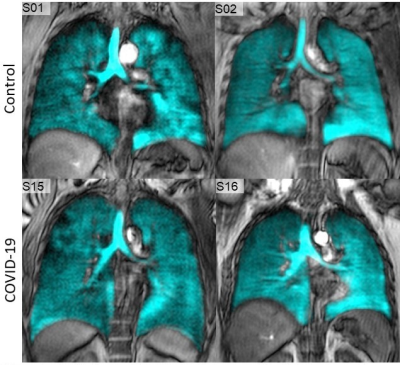
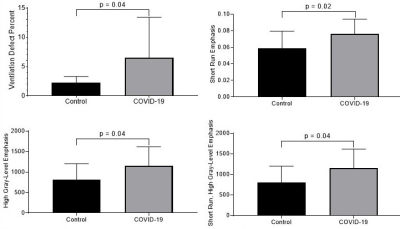
129Xe MRI ventilation texture features differentiate long-haul COVID-19 and never-infected participants. This will frame a study of moderate-severe COVID-19 survivors to identify those that may experience long-term symptoms related to COVID-19.