Simone Rumac1, Christopher W. Roy2, Jérôme Yerly2,3, John Heerfordt2,4, Davide Piccini2,4, Matthias Stuber3,5, and Ruud B. van Heeswijk2
1Department of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne (UNIL), Laus, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Department of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne (UNIL), Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3CIBM Center for BioMedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland, 4Advanced Clinical Imaging Technology, Siemens Healthcare AG, Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland, 5Department of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
1Department of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne (UNIL), Laus, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Department of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne (UNIL), Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3CIBM Center for BioMedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland, 4Advanced Clinical Imaging Technology, Siemens Healthcare AG, Lausanne, Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland, 5Department of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
We
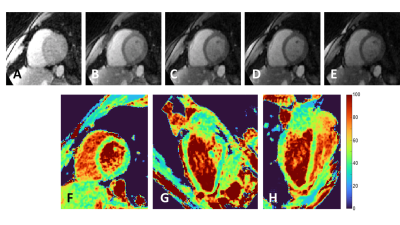
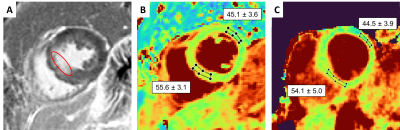
developed a novel fast high-resolution free-breathing 3D isotropic T2
mapping technique for the heart. The resulting whole-heart T2 maps
were both accurate and sharp, and the T2 values in the myocardium matched
those measured with routine 2D T2 mapping (p=0.57).