Martins Otikovs1, Ankit Basak1, and Lucio Frydman1
1Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
1Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
The benefits of performing locally low-rank (LLR) reconstruction on
subsampled diffusion weighted (DW) data employing spatiotemporal
encoding (SPEN) methods, is investigated. Additional improvements are demonstrated when using LLR with subspace constrained reconstruction.

Figure 3. Left: ACR phantom images for 6 b-values, each of them reconstructed from a set of six interleaved SPEN data acquisitions following the processing described in Ref. 8. Center: Idem but from a set of undersampled data, using only one of the interleaved scans per b-value and following Eq. (2). Right: ADC maps calculated from b=0 and 800 s/mm2 DW images by both methods. For the subspace LLR reconstruction diffusion was modeled using K=2 eigenvectors after SVD of monoexponential functions modeling signal attenuation as function of b for ADCs in the 0.1-5x10-3 s/mm2 range.
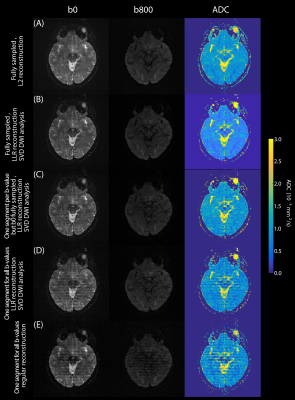
Figure 5. Comparing different strategies for processing a 6-b-value (0-1000 s/mm2) SPEN experiment. (A) Usual DWI reconstruction, illustrating two b-valued images and the resulting ADC map.8 (B) Same but with constrained DW subspace LLR reconstruction on the full set. (C) Idem as in B, but for data with a fully sampled b=0 image and only one shot for the other b’s. (D) Idem as C, but a single shot also used for the b=0 image reconstruction. (E) Same as D, but using reconstruction in Ref. 10. Data in B-E were obtained undersampling acquisition of 6 segments at 1.2x1.2x3 mm3 resolution.