Gregory Lemberskiy1, Dmitry S Novikov1, Mary Bruno1, Mahesh Bharath Keerthivasan2, Els Fieremans1, and Hersh Chandarana1
1Radiology, NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Siemens Medical Solutions, New York, NY, United States
1Radiology, NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Siemens Medical Solutions, New York, NY, United States
We compared standard and RMT reconstructions for a prostate DWI exam on a prototype 0.55T for varying number of averages (1 to 40) to evaluate the image quality and overall loss.
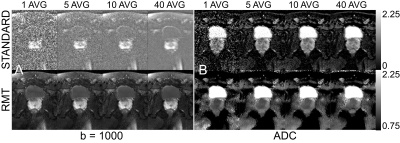
DWI at 0.55T. We compare [1,5,10,40] averages of (A) b=1000 and (B) ADC images for standard and RMT reconstructions. ADC images are scaled differently, as the Rician bias of standard images dramatically lowers ADC.
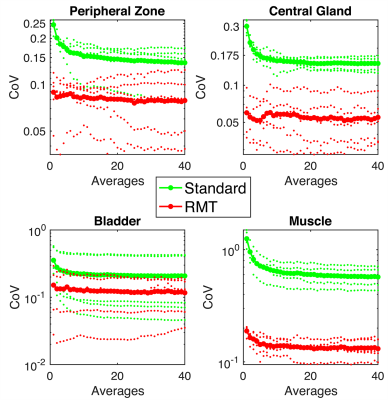
Coefficient of Variation (CoV) [std(ADC)/mean(ADC)] in ADC as a function of the number of averages compared between standard (green) and RMT(red). The smaller dots represent individual cases, whereas the larger dots represent the median CoV curve. RMT consistently shows lower CoV than the standard recon, even suggesting that variance due to noise can be minimized with this approach. For both reconstructions, CoV decreases with number of averages (except for cases with small ROIs [peripheral zone, lesion] due to motion between averages).