Negin Yaghmaie1,2, Warda Syeda3,4, Chengchuan Wu1,2, Yicheng Zhang1,2, Bradford A. Moffat1,4, Rebecca Glarin1,5, Scott Kolbe4,6,7, and Leigh Johnston1,2
1Melbourne Brain Centre Imaging Unit, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 3Melbourne Neuropsychiatry Centre, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 4Department of Medicine and Radiology, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 5Department of Radiology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia, 6Department of Neuroscience, Central Clinical School, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 7Department of Radiology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
1Melbourne Brain Centre Imaging Unit, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 3Melbourne Neuropsychiatry Centre, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 4Department of Medicine and Radiology, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 5Department of Radiology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia, 6Department of Neuroscience, Central Clinical School, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 7Department of Radiology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
QSMART showed successful reduction of streaking artifacts as well as improved contrast between different brain tissues compared to the QSM maps obtained by RESHARP/iLSQR and V-SHARP/iLSQR. The artifact reduction in QSMART enables more robust estimation of susceptibility values in vivo.
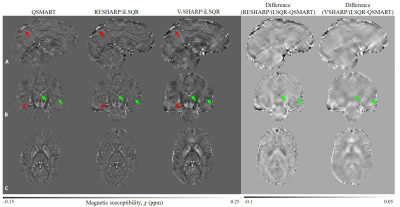
Single Orientation QSM results from QSMART, RESHARP/iLSQR and V-SHARP/iLSQR, and the difference maps between the susceptibility values calculated by QSMART and the two other methods. Dark cortical surface artifacts (red arrows) and x-shaped artifacts caused by veins and high susceptibility sources (green arrows) are successfully suppressed by QSMART.