Simon Sun1, Ek Tsoon Tan1, John A Carrino1, Douglas Nelson Mintz1, Meghan Sahr1, Yoshimi Endo1, Edward Yoon1, Bin Lin1, Robert M Lebel2, Suryanarayan Kaushik2, Yan Wen2, Maggie Fung2, and Darryl B Sneag1
1Radiology, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, United States
1Radiology, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, United States
Interobserver agreement for variables of interest among 3D T2w-FSE DLRecon
and SOC reconstructions and SOC 2D T2w-FSE ranged from moderate to very good,
and was similar for all three sequences. Overall image quality was
qualitatively improved on 3D T2w-FSE using DLRecon.
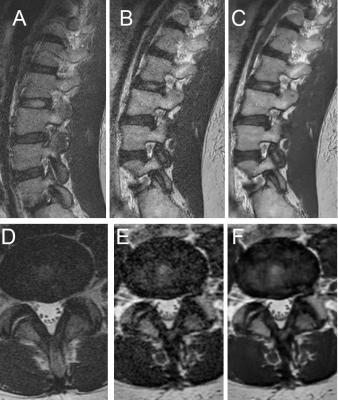
Fig. 2 Top Row, sagittal T2-weighted images of
the lumbar spine categorized by sequence demonstrated markedly improved image
quality using the DLRecon
algorithm for 3D imaging:
A:
2D T2 standard of care (SOC) T2-weighted fast spin echo (T2w-FSE) B: 3D
standard of care (SOC) T2w-FSE C: Deep learning reconstructed (DLREcon) 3D
T2w-FSE
Bottom Row, axial T2-weighted images of
the lumbar spine, categorized by sequence, demonstrate superior image quality
with the DLRecon
algorithm for 3D imaging:
D: 2D T2 standard of care (SOC) E: 3D SOC
T2w-FSE F: DLRecon 3D
T2w-FSE