Deepa Anand1, Dattesh Shanbhag1, Preetham Shankpal1, Chitresh Bhushan2, Desmond Teck Beng Yeo2, Thomas K Foo2, and Radhika Madhavan2
1GE Healthcare, Bangalore, India, 2GE Global Research, Niskayuna, NY, United States
1GE Healthcare, Bangalore, India, 2GE Global Research, Niskayuna, NY, United States
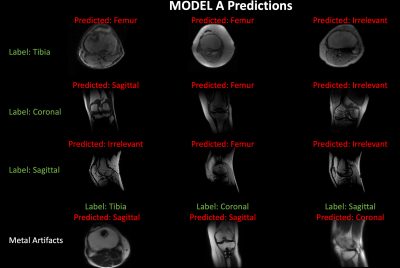
Grad-CAM activation maps were used to generate simulated images with relevant regions corrupted to mimic image variations. Training with the proposed data augmentation framework resulted in improved performance and robustness of knee MRI classification, even in presence of metal implants.
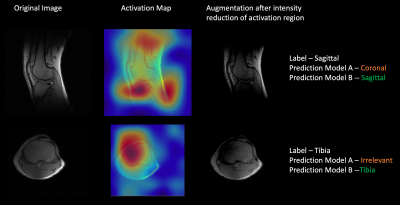
Figure 2: Grad-CAM map highlights region of interest to classify slice indicating the femoral condyle region. The inverted Grad-CAM map was used to obfuscate the region of interest (femoral condyle) to generate adversarial augmented image. Notice how these variations in intensity could easily mimic for example, RF intensity bias or coil failure. Testing on these augmented images resulted in misclassification in the prediction using the model trained on normal images (Model A), but were correctly classified when trained on adversarial augmented images (Model B).