Qingle Kong1,2, Yue Wu1, Dehe Weng3, Jing An3, Yan Zhuo1,4, and Zihao Zhang1,4
1Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China, 4The Innovation Center of Excellence on Brain Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
1Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China, 4The Innovation Center of Excellence on Brain Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
The inner-volume 3D TSE sequence with optimized spatially selective excitation RF pulses was developed to achieve isotropic 0.30 mm black-blood images within ten minutes for the first time. The IV-SPACE images showed clearer delineation of vessel wall of LSA than conventional SPACE images.
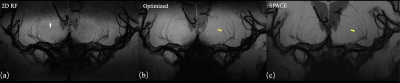
Figure 4. Coronal MinIP images of 2D RF (a), optimized method (b), and conventional SPACE (c). The optimization method achieves more thorough signal suppression compare to traditional 2D RF and suffer from fewer aliasing artifacts (white arrow). Due to the increase in spatial resolution, the optimized method shows more branches that are invisible to conventional SPACE images (yellow arrows).
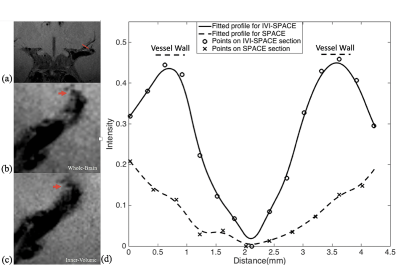
Figure 5. The comparisons of IV-SPACE and conventional SPACE in the coronal plane. The enlarged images were shown on the right side. The lumen and orifice of an LSA are clearly depicted in the IV-SPACE image, whereas the lumen and orifice of the vessel were blurred in conventional SPACE. The depiction of the LSA vessel wall of IV-SPACE is also better than conventional SPACE.