Marco Barbieri1, Akshay S. Chaudhari1,2, Catherine J. Moran1, Garry E. Gold1,3, Brian A. Hargreaves1,3,4, and Feliks Kogan1
1Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Biomedical Data Science, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
1Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Biomedical Data Science, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
The proposed method for measuring B0 inhomogeneities from a qDESS
acquisition provided B0 maps that were in good agreement with those
obtained using WASSR both in phantom and in-vivo. The agreement between qDESS
and WASSR was comparable to that of a standard 2-GRE method.
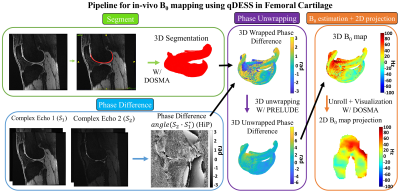
Schematization of the
processing pipeline used to compute B0 map in Femoral Cartilage using qDESS.
The coil-combined phase difference between the second and first echo is
computed using the Hermitian inner product10. Femoral cartilage is
segmented using a deep learning model with the DSOMA framework13.
The FC segmented 3D wrapped phase difference is unwrapped with PRELUDE14
and then B0 is computed according to eq. 1. The 3D B0 map is projected onto a
2D space for visualization using DOMSA.
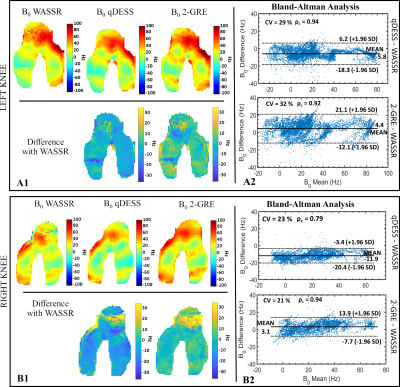
Left (A1) and right
(B1) unrolled 2D B0 projection maps in FC obtained using the WASSR, qDESS and
2-GRE methods for a simultaneous bilateral knee acquisition. A pixel-wise
unrolled 2D difference map with WASSR is also displayed. BA plots for the left
(A2) and right (B2) knees to evaluate the agreement between the WASSR method and the qDESS and 2-GRE methods, respectively. The plots
were made using B0 values sampled from six slices in the FC (2 in the lateral
condyles, 2 in the trochlea, and 2 in the medial condyles). In the right knee, registration errors caused
artifacts in the trochlea region.