Xinzhou Li1,2, Yu-Hsiu Lee3, David S. Lu1, Tsu-Chin Tsao3, and Holden H. Wu1,2
1Radiological Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
1Radiological Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
This work used a deep learning-based needle localization algorithm in a new automatic workflow to realign the MRI scan plane with the needle. In one degree-of-freedom needle insertion experiments, the MRI scan plane was rapidly and accurately aligned with the needle.
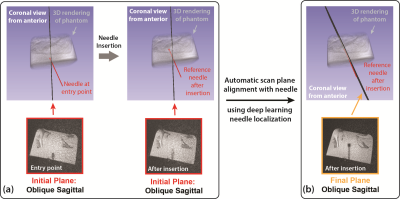
Figure 4: (a) The needle feature at the entry point and after insertion were displayed for initial plane. The incomplete needle feature after insertion was caused by misalignment between the initial plane with the needle trajectory. Orientation difference (dθ) and Hausdorff distance (HD) are 19.2° and 13.9 mm. The reference needle was extracted by segmenting needle feature on a high-resolution 3D confirmation scan. (b) After executing the proposed automated workflow, the final plane was aligned with the needle and the complete needle feature is visible. dθ and HD were 1.8° and 1.8 mm.
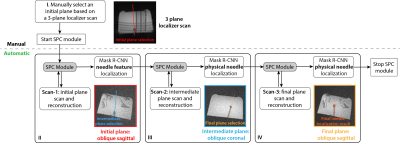
Figure 2: The workflow for automatic MRI scan plane alignment with the needle using Mask R-CNN and the scan plane control (SPC) module. (I) An initial plane was manually selected based on the needle feature at the entry point on 3-plane localizer images. (II-IV) Scans 1-3 automatically started using the plane selection from the previous step. Mask R-CNN needle localization results were used to automatically select a new plane that aligned with the needle.
