Makoto Obara1, Osamu Togao2, Tatsuhiro Wada3, Chiaki Tokunaga3, Ryoji Mikayama3, Hiroshi Hamano1, Kim van de Ven4, Masami Yoneyama1, Tetsuo Ogino1, Yuta Akamine1, Yu Ueda1, Jihun Kwon1, and Marc Van Cauteren5
1Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Molecular Imaging & Diagnosis, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 3Division of Radiology, Department of Medical Technology, Kyushu University Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands, 5Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan
1Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Molecular Imaging & Diagnosis, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 3Division of Radiology, Department of Medical Technology, Kyushu University Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands, 5Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan
The feasibility of multiple repetition time scheme
with dynamically optimized background suppression (BGS) in pseudo continuous
arterial spin labeling was suggested. Reliable background suppression
effectiveness and a significant SNR gain were confirmed in healthy volunteers.
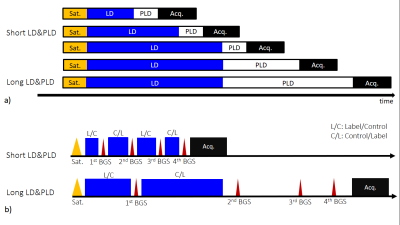
Figure 1: multi-TR scheme: a) Schematic drawings of the multi-TR scheme without BGS . Data acquisition at each time point consists of presaturation (Sat.), and control or label modules (LD) followed by data acquisition (Acq.). ASL dynamics data are acquired by changing the LD and PLD in each session. b) The BGS timing optimization for the short and long time point acquisition. Four BGS pulses are inserted in LD and PLD. Label or control module is changed with interleaved manner (L/C to C/L) with BGS pulse insertion.
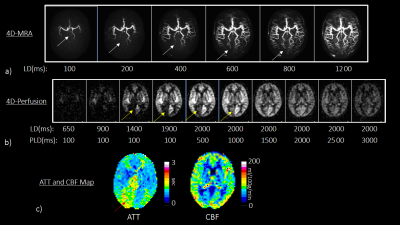
Figure 5: Representative
Volunteer case of fetal type: a) 4D MRA (separate acquisition) and b) 4D
perfusion results with background suppression, and c) ATT and CBF map
calculated from the individual timepoints in 4D perfusion. The left
and right ATT difference in PCA territory is indicated by 4D-MRA (white
arrows). In the ASL dynamic, the flow signal is increased
earlier in the left PCA territory compare to the right PCA territory (yellow
allows). The ATT map shows longer ATT in the right PCA territory (red arrow).
These observations are consistent with the 4D-MRA findings.