Paul Dubovan1,2, Lars Kasper3, Kamil Uludag3,4, and Corey Baron1,2
1Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Center for Functional and Metabolic Mapping, Robarts Research Institute, London, ON, Canada, 3Techna Institute, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
1Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Center for Functional and Metabolic Mapping, Robarts Research Institute, London, ON, Canada, 3Techna Institute, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
We investigate the effects of signal undersampling and static field map resolution for single-shot spiral diffusion MRI acquisitions, which showed optimized image quality for a moderate acceleration factor and the highest field map resolution.
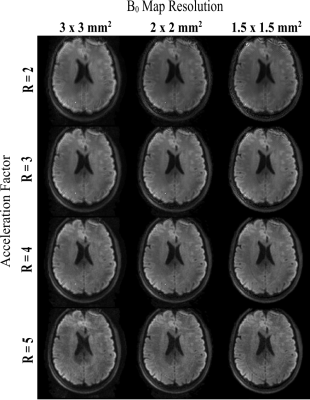
FIG. 3. Mean
DWI maps of a sample slice created from 6 different diffusion-encoding
directions (b = 1000 s/mm2), acquired with acceleration factors R =
2-5, and varying field map resolutions.
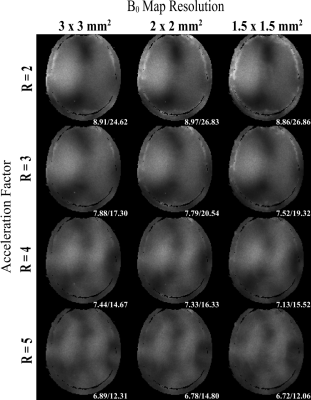
FIG. 4.
Noise SD maps for acceleration factors of R = 2-5, and isotropic field map
resolutions of 3 mm, 2 mm, and 1.5 mm. Maps created by calculating the SD of
100 b0 image replicas and scaled inversely by the square root of R. Numbers
below maps indicate the mean/maximum noise SD of brain and skull components. All values shown are truncated and are to be multiplied by a factor of 10-6 to show the full values.
