Edwin Eduard Gert Willem ter Voert1, Florian Wiesinger2, Graeme McKinnon3, Mathias Engström4, Jose Fernando de Arcos5, Marlena Hofbauer1, Ronny R Buechel1, and Philipp A Kaufmann1
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2GE Healthcare, Munich, Germany, 3GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, United States, 4GE Healthcare, Stockholm, Sweden, 5GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, Amersham, United Kingdom
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2GE Healthcare, Munich, Germany, 3GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, United States, 4GE Healthcare, Stockholm, Sweden, 5GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, Amersham, United Kingdom
In the current study we demonstrate that ZTE imaging on PET/MR, combined
with Deep Learning reconstructed ZTE, can likely be applied to detect
calcifications in peripheral vasculature.
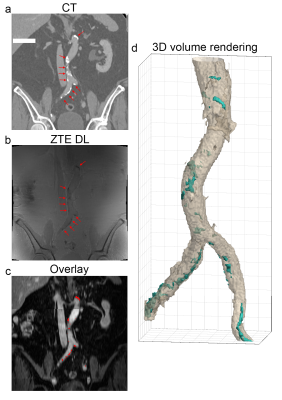
Figure 2: Example coronal slices and a 3D volume rendering in the
abdominal region. a) prior obtained CT, b) Deep Learning reconstructed ZTE, c)
ZTE calcifications (red) overlaid on the contrast enhanced water map MRI
(LAVA-Flex based), d) 3D volume rendering showing the ZTE calcifications (cyan).
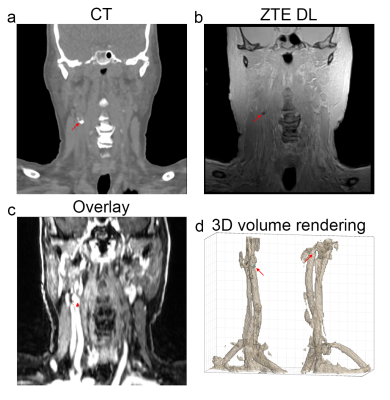
Figure 4: Example coronal slices and a 3D volume rendering in the
head/neck region. a) prior obtained CT with indicated (red arrow) calcification,
b) Deep Learning reconstructed ZTE, c) ZTE calcifications (red) overlaid on the
contrast enhanced water map MRI (LAVA-Flex based), d) 3D volume rendering
showing the ZTE calcifications (cyan).
