Timothy Allen1,2, Leah C Henze Bancroft2, Lloyd Estkowski3, Ty A Cashen3, Frederick Kelcz2, Frank R Korosec1,2, Roberta M Strigel1,2,4, Orhan Unal1,2, and James H Holmes2
1Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States, 4Carbone Cancer Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
1Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 3Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States, 4Carbone Cancer Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
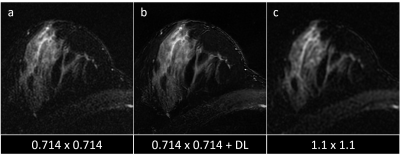
A deep
learning reconstruction was found to increase perceived signal-to-noise ratio,
sharpness, and overall image quality in T2w breast MRI. Preliminary results show that deep learning can help reverse image degradation associated with rapid high-resolution imaging.
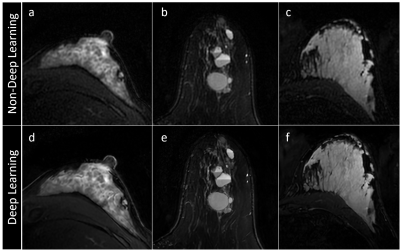
Figure 1: Axial T2w breast MR images reconstructed with deep learning scored significantly higher in SNR and image sharpness than those without deep learning. (a,d) A patient with substantial
fibroglandular tissue; (b,e) a patient with multiple simple and complicate cysts; and (c,f) a lactating
patient.