Charles Millard1,2, Aaron T Hess2, Jared Tanner1, and Boris Mailhe3
1Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2Oxford Centre for Clinical Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3Digital Technology and Innovation, Siemens Healthineers, Princeton, NJ, United States
1Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2Oxford Centre for Clinical Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3Digital Technology and Innovation, Siemens Healthineers, Princeton, NJ, United States
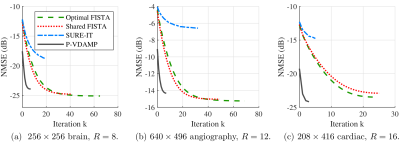
We present the Parallel Variable Density Approximate Message Passing (P-VDAMP) algorithm for compressed sensing MRI, and find that it converges to a mean-squared error similar to optimally
tuned FISTA, but in
around 5x fewer iterations and without the need to tune model
parameters.
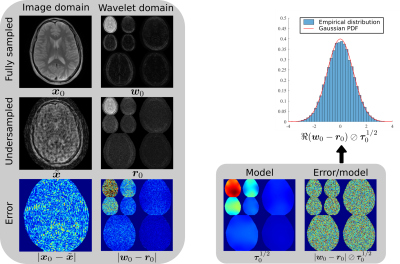
Fig 2. The aliasing of a zero-filled, density compensated estimate in the image and wavelet domains of a tenfold undersampled brain, and the wavelet-domain aliasing estimate $$$\boldsymbol{\tau}_0$$$. The histogram verifies that $$${\boldsymbol{r}}_0 \approx \boldsymbol{w}_0 + \mathcal{CN}(\boldsymbol{0}, \text{Diag}(\boldsymbol{\tau}_0))$$$ is an accurate model of the aliasing.