Jiaqi Dou1, Yajie Wang1, Huiyu Qiao1, Zhensen Chen1, Yuze Li1, Haikun Qi2, Jie Sun3, Dongxiang Xu3, Xihai Zhao1, and Huijun Chen1
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Department of Radiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States
1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Department of Radiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States
This study generated a set of co-registered T1w, T2w, PDw images, and MRA based on a SIMPLE sequence. Preliminary experiments validated the feasibility of the generated multi-contrast images for carotid plaque assessment and comparable performance with conventional sequences.
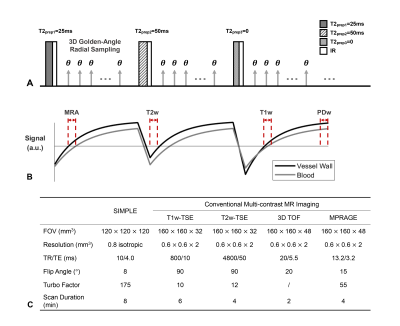
Figure 1
A, Sequence diagram of SIMPLE, in which
three alternate T2-prep pulses of 25, 50,
and 0 ms and
IR pulses, incorporated with 3D golden-angle
radial acquisition, are adopted. B,
Simulated signal evolutions of the vessel wall and blood within three continuous
shots with different T2-prep pulses.
And the illustration of view sharing
and sliding window reconstruction
of the generated multi-contrast images from SIMPLE, including MRA, T1w, T2w and
PDw images. C, Scan parameters of SIMPLE and conventional multi-contrast MR imaging.
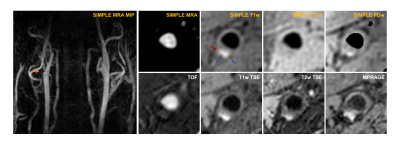
Figure 2 An example of the generated MRA
as well as axial MRA, T1w, T2w, and PDw images by
SIMPLE from one patient
with atherosclerotic plaques,
with comparison to the conventional sequences. Coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP)
of MRA
demonstrated
clear
depictions of bilateral carotid arteries. IPH (red
arrow)
showed hyperintensity on
both SIMPLE-T1w image and T1w TSE image. Blue arrows indicated
the hypointensity of calcification.