Bart R. Steensma1, Cornelis A.T. van den Berg1, and Alexander J.E. Raaijmakers2
1Center for Image Sciences - Computational Imaging Group, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Biomedical Engineering - Medical Imaging Analysis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, Netherlands
1Center for Image Sciences - Computational Imaging Group, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2Biomedical Engineering - Medical Imaging Analysis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, Netherlands
By using a PPU during MR Thermometry, we were able to perform reproducible thermometry measurements of in vivo local temperature rise of less than 1 °C
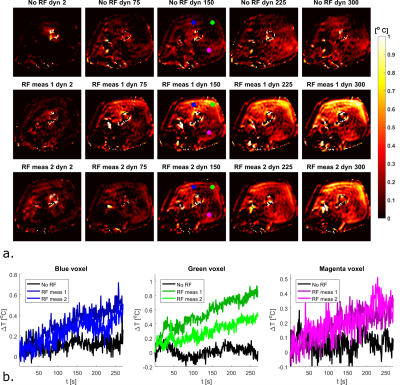
Figure 4: 4a. spatial maps of temperature rise
calculated from MRT measurements after drift correction. The images in the top
row were acquired with no RF heating, while the images on the two bottom rows
were acquired with the same RF shim. 4b. Time series of temperature change in
the indicated voxels for all 3 measurements.
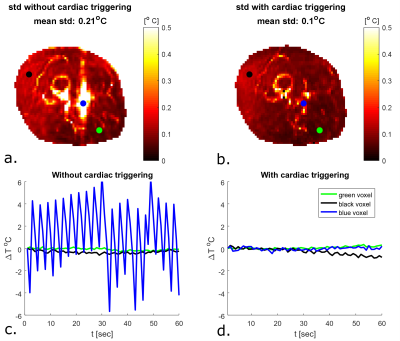
Figure 3: 3a and 3b. Spatial maps of temporal standard
temperature deviation the upper leg during a MRT scan where no RF heating
is applied, without and with cardiac triggering. 3c and 3d. Time series of
temperature deviations in indicated voxels (3a and 3b). No drift correction was applied yet during this short time interval.
