Malte Roehl1,2, Peter D Gatehouse1,2, Pedro F Ferreira1,2, Sonya V Babu-Narayan1,2, David N Firmin1,2, Dudley J Pennell1,2, Sonia Nielles-Vallespin1,2, and Andrew D Scott1,2
1National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Unit, Royal Brompton Hospital, London, United Kingdom
1National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Unit, Royal Brompton Hospital, London, United Kingdom
Ex-vivo diffusion tensor cardiovascular magnetic resonance provides insights into cardiac microstructure and validation of in-vivo methods. To overcome limitations of current EPI methods we present an interleaved spiral approach, yielding good image quality at high resolution.
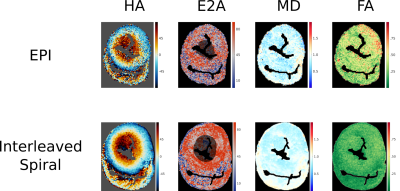
Figure 5:Comparison
of HA, E2A, MD and FA for a single midventricular slice in a porcine ex vivo
heart using a spiral readout and an EPI readout. Both using the same STEAM
approach, multiple averages (both using complex averaging) and the same total
acquisition time of 2hours.
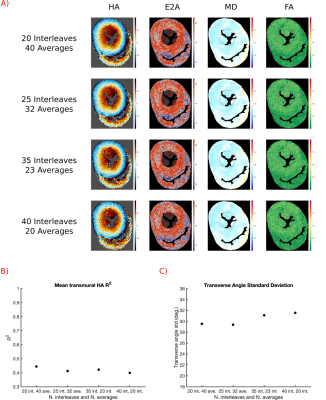
Figure 4:A)
DT-CMR maps reconstructed from data acquired with similar total acquisition
duration, but increasing numbers of spiral interleaves/decreasing numbers of interleaves.
Total acquisition time was 2h for rows 1-4. B) Plot of mean transmural HA-R2
of the data shown in A. C) Plot of Transverse Angle standard deviation of the
data shown in A.