1Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), Braunschweig and Berlin, Germany
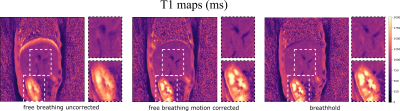
Figure 4: The motion corrected T1 maps show an increase in image quality. Respiratory blurring especially at the dome of the liver and around blood vessels could be reduced yielding similar image quality than the breathholdscan. Although the motion model was built for the liver, also the visualization of the kidneys is improved. It should be noted, that the breathhold data cannot be directly compared to motion corrected images, because they were acquired in two separate scans.
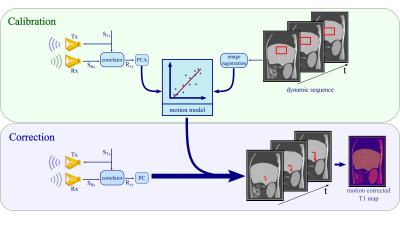
Figure 1: Calibration: The M-sequence STx gets transmitted by a sending antenna Tx and correlated with the received response SRx to create an impulse response Rxy. The principal components of Rxy get linearly fitted to the registered changes in a selected region of interest in the dynamic scan. Correction: Based on the motion model, radar signals obtained simultaneously to the T1 mapping sequence are used to predict respiratory motion shifts which can then be utilized during image reconstruction to correct for motion artefacts.
