Zhongliang Zu1, Fatemeh Adelnia1, Kevin Harkins1, Feng Wang1, and John Gore1
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States
Spin-lock imaging at low locking amplitudes may provide information on tissue microvasculature. But there are residual errors in estimates of R1ρ even if composite pulse preparations are used. In this work, we developed an
approximate theoretical analysis to correct these errors.
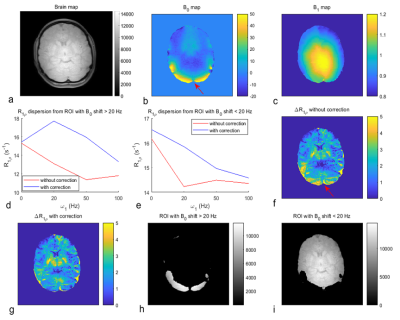
FIG.3 Maps of brain (a), B0 (b), B1
(c), and ΔR1ρ (the
subtraction of two R1ρ maps acquired with ω1 of 0 and 100Hz), without/with
correction (f, g) from a healthy human subject. (d, e) show the averaged R1ρ
dispersions without/with correction from the ROI with large B0 shift
(│Δωoff│ > 20 Hz) (h) and small B0 shift (│Δωoff│
< 20 Hz) (i), respectively.
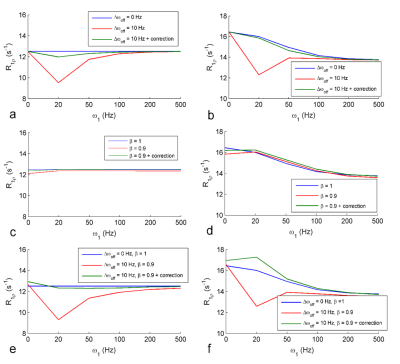
FIG. 2. Single-pool (a, c, e) and
two-pool (b, d, f) model simulated R1ρ dispersions under B0 shift (a, b), B1 shift (c,
d), and both B0 and B1 shift (e, f), and with correction
(green lines) and without correction (red lines). R1ρ dispersions with no shifts in either B0 or B1
(blue lines) were also plotted for comparison. Simulation parameters
included T1a=1.5s, T2a=80ms, T1b=1s, T2b=30ms;
fractional concentration of pool B is 0.2; the exchange rate from pool B to
pool A is 20s-1; resonance frequency of pool A is 0 Hz and pool B is
63.5 Hz.