Jing Liu1, Hailong Li1, Lingxiao Cao1, Xue Li2, Suming Zhang1, and Xiaoqi Huang1
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and molecular imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and molecular imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
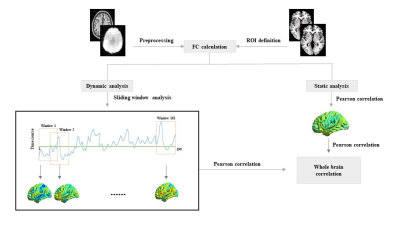
The BNST demonstrated different connected regions in sFC and dFC in OCD,
indicating their combination can provide more comprehensive information by
considering both the static and time-varying aspects.
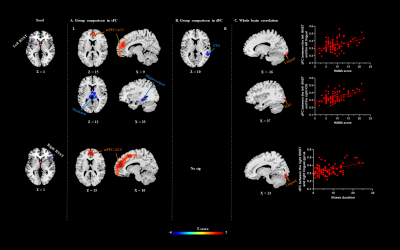
Figure
2. Brain regions with significant group difference
between OCD and HC in sFC (A) and dFC (B). Warm/cool colors indicate regions
showing higher/lower sFC/dFC value in the OCD group comparing with HC. The HAMA score positively correlated with dFC
between the left BNST and the left lingual gyrus, and the right IOG. The
illness duration positively correlated with dFC between the right BNST and
right lingual gyrus (C). The warm colors indicate regions showing positive
correlation with clinical scores. IOG, inferior occipital gyrus; HAMA, Hamilton
Anxiety Rating Scale.