Betty Chinda1,2, Simon Liang3, William Siu4, George Medvedev5, and Xiaowei Song1,2
1Department of Biomedical Physiology & Kinesiology, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2Health Research and Innovation, Fraser Health Authority, Surrey, BC, Canada, 3Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Department of Radiology, Royal Columbian Hospital, New Westminster, BC, Canada, 5Department of Neurology, Royal Columbian Hospital, New Westminster, BC, Canada
1Department of Biomedical Physiology & Kinesiology, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2Health Research and Innovation, Fraser Health Authority, Surrey, BC, Canada, 3Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Department of Radiology, Royal Columbian Hospital, New Westminster, BC, Canada, 5Department of Neurology, Royal Columbian Hospital, New Westminster, BC, Canada
This study provides the first task-phase fMRI evidence demonstrating that the standard clinical carotid angioplasty and stenting leads to improvements in cognitive function in the re-perfused vascular territory in patients with severe carotid stenosis, in addition to stroke prevention.
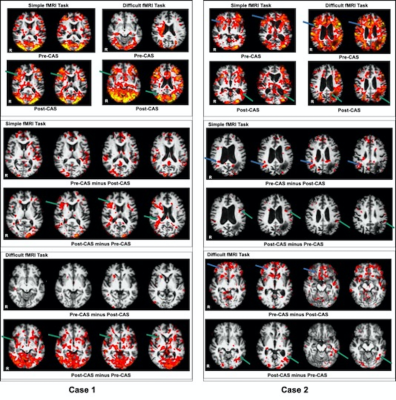
FMRI activation maps: Z statistic images were thresholded using clusters determined by Z>2 (P=0.05). The top panel shows comparison of brain activation of the simple and difficult tasks (pre-and post-CAS); the middle and bottom panels shows subtraction images of the two time-points for the simple and difficult tasks respectively.Case 1 (left) had more activations in the treated right hemisphere post-CAS (green arrows). Case 2 (right) had more fMRI activations post-CAS in the treated left hemisphere (green arrows) and reduced in the contralateral hemisphere (blue arrows).
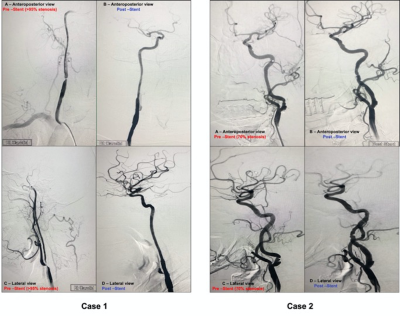
Carotid angiogram pre-and post-stenting in anteroposterior and lateral projections: The left figure shows the carotid angiogram for Case 1 with right carotid artery flow-limiting stenosis (>95%, determined using NASCET criteria) while the right figure shows Case 2 with left carotid artery non-flow-limiting stenosis (70%, NASCET criteria). The top and bottom panels show the anteroposterior and lateral projections respectively. In each panel, the left image shows the pre-CAS stenotic artery while the right image shows the post-CAS artery with the stent implanted.