Yunyun Jiao1, Jie Gong1, Hui Deng1, Dongchen Sun1, and Wei Qin1
1Engineering Research Center of Molecular and Neuro Imaging of the Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi'an, China
1Engineering Research Center of Molecular and Neuro Imaging of the Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi'an, China
Temporal variability of resting state functional
connectivity may serve as a promising indicator to predict the response to ECT in patients with SZ.
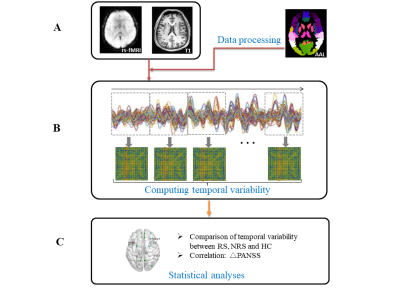
Figure 1.Flow chart of data processing and analysis. A) fMRI
data used in this research. B) We
extracted time courses from each ROI of the anatomical automatic labeling
atlas-90 (AAL-90) mask and
calculated the temporal variability of each region. C) Statistical analysis was
performed, including grouping comparison of temporal variability of RS, NRS and
HC, and Pearson correlation analysis to reveal the relationship between temporal
variability and ΔPANSS.
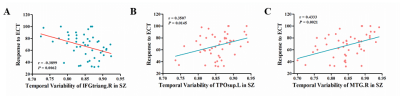
Figure 2.The relationship between the response to ECT (△PANSS)
and the temporal variability in brain regions of discriminant differences in
SZ. A) The temporal variability of IFGtriang.R in RS is negatively correlated
with the response to ECT. The temporal variability of TPOsup.R B) and MTG.R C)
in NRS is positively correlated with the response to ECT.
