WeiJie Bao1, YingXue Gao1, Hailong Li1, jing Liu1, Lingxiao Cao1, Xuan Bu1, and Xiaoqi Huang1
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and Molecular Imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Functional and Molecular Imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
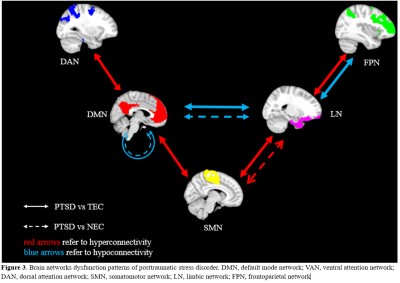
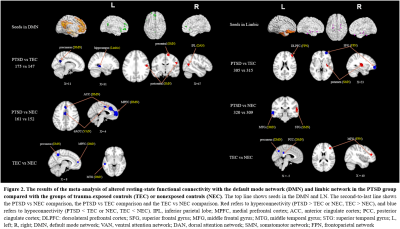
Our findings suggested that the long-lasting effect of trauma on
the function of the default mode network (DMN) and limbic network (LN)
regardless of whether it caused symptoms of PTSD.