Patcharaporn Srisaikaew1,2, Jordan A. Chad3,4, Pasuk Mahakkanukrauh1,5, Nicole D. Anderson3,6, and J. Jean Chen3,4
1Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2PhD Program in Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 3Rotman Research Institute, Baycrest Health Centre, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5Excellence in Osteology Research and Training Center (ORTC), Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 6Department of Psychology and Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
1Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2PhD Program in Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 3Rotman Research Institute, Baycrest Health Centre, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5Excellence in Osteology Research and Training Center (ORTC), Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 6Department of Psychology and Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
The difference between nondemented ApoE4+ and ApoE4- in the age-association of DTI metrics were most present in posterior WM regions. MO and NA showed more sensitivity to age than conventional DTI metrics, especially in crossing fibres.
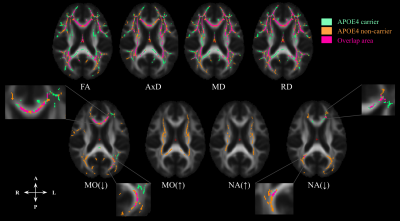
Figure 1. The overlap map of the significant associations between DTI metrics with increasing age across the whole-brain WM in nondemented ApoE carrier (ApoE4+, green), ApoE4 non-carrier (ApoE4-, orange), and both groups (Overlap, pink) at p < 0.05. Note: MO is increasing with age, MO(↑); MO is decreasing with age, MO(↓); NA is increasing with age, NA(↑); NA is decreasing with age, NA(↓).
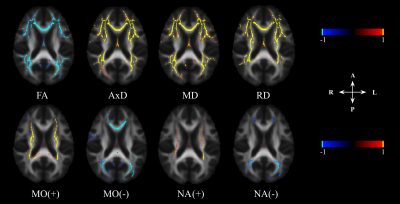
Figure 2. Significant associations between DTI metrics with increasing age across the whole-brain WM in nondemented ApoE non-carrier (ApoE4-) group at p < 0.05. The colour bar shows the negative (blue) and positive (yellow) correlation between DTI metrics with age. Note: MO is increasing with age, MO(↑); MO is decreasing with age, MO(↓); NA is increasing with age, NA(↑); NA is decreasing with age, NA(↓).