Jesus E. Fajardo1 and Gonzalo A. Álvarez1,2,3
1Centro Atómico Bariloche, CONICET, CNEA, 8400, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina, 2Instituto Balseiro, CNEA, Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, 8400, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina, 3Instituto de Nanociencia y Nanotecnología, CONICET, CNEA, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina
1Centro Atómico Bariloche, CONICET, CNEA, 8400, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina, 2Instituto Balseiro, CNEA, Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, 8400, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina, 3Instituto de Nanociencia y Nanotecnología, CONICET, CNEA, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina
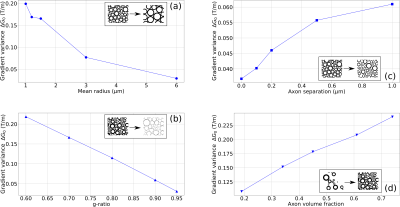
We predict the potential of extracting structural parameters of axon models measuring the variance of internal gradient distributions with modulated gradient spin echo sequences.
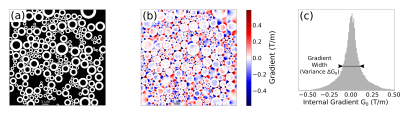
Fig 1: Axon distribution and internal gradient simulations. (a) Matrix encoding with ones (myelin sheath) and zeros (intra and extra axonal water) describing the axonal structure. (b) Internal Gradient G0 component along the x axis. (c) Histogram of the x axis internal gradient component. The histogram width is given by the standard deviation of the G0 strength distribution.