Juan Luis Villarreal Haro1,2, Gabriel Girard1,3,4, Jean Philippe Thiran1,4, and Alonso Ramírez-Manzanares2
1Signal Processing Lab (LTS5), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Computer Science Department, CIMAT, Centro de Investigación en Matemáticas, Guanajuato, Mexico, 3CIBM Center for BioMedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, 4Radiology Department, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
1Signal Processing Lab (LTS5), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Computer Science Department, CIMAT, Centro de Investigación en Matemáticas, Guanajuato, Mexico, 3CIBM Center for BioMedical Imaging, Lausanne, Switzerland, 4Radiology Department, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Our proposal improves the connectome identification from the same subject regardless of the variability in the construction. The detected structural changes between subjects could be used to distinguish structural changes associated with diseases.
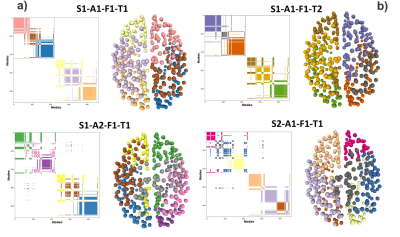
Figure 1. The Community Matrix (CoMi) is defined as the entry [n1,n2] =1 if the nodes n1 and n2 belong to the same community, otherwise zero. In the matrices visualization, white is zero, and the colors are one. Different colors represent different network communities. Note that the connectomes generated S1-A1-F1-T2 and S1-A1-F1-T2 only differ by tractography (T1 and T2), but they are not identical. They are as different as the CoMi of a different Subject S2-A1-F1-T1.
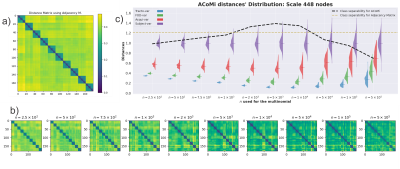
Figure 3 a) Matrix distances for the 180 connectomes constructed by using the L_{1,1} norm between adjacency matrices [2]. b) New distance matrices for ACoMi are generated for different $n$, c) for every distance matrix, the comparisons are reported separately: Traco-var, FOD-var, Acqui-var, and Subject-var. An optimization procedure is executed to estimate the $n$ that maximizes the geometric mean of the FDC (Fisher Discriminant Coefficient) and the mean error in the distributions.
