Zhoubing Xu1, Guillaume Chabin2, Robert Grimm3, Stephan Kannengiesser3, Li Pan4, Vibhas Deshpande5, Gregor Thoermer3, Sasa Grbic1, and Cara Morin6
1Siemens Healthineers, Princeton, NJ, United States, 2Siemens Healthineers, Paris, France, 3Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany, 4Siemens Healthineers, Baltimore, MD, United States, 5Siemens Healthineers, Austin, TX, United States, 6St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, United States
1Siemens Healthineers, Princeton, NJ, United States, 2Siemens Healthineers, Paris, France, 3Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany, 4Siemens Healthineers, Baltimore, MD, United States, 5Siemens Healthineers, Austin, TX, United States, 6St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, United States
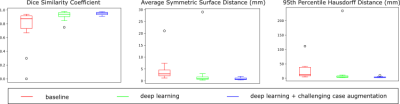
A deep learning-based solution was developed for liver segmentation on T1-weighted MRI with improved performance compared to a commercially available solution and robustness on a challenging cohort of pediatric patients including cases with high iron content.
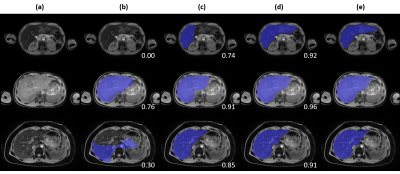
Figure 4. Qualitative
comparison across tested approaches on three representative cases. (a) T1-weighted
water image, (b) baseline approach, (c) deep learning approach, (d) deep
learning with pediatric and high iron case augmentation, (e) manual annotation.
DSC against manual annotation is provided at the bottom left corner for each
case of (b, c, d).