Weijie Gan1, Yu Sun1, Cihat Eldeniz2, Jiaming Liu3, Hongyu An2, and Ulugbek S. Kamilov1,3
1Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States, 2Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States, 3Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States
1Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States, 2Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States, 3Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, United States
An unsupervised deep learning method for MRI that simultaneously addresses the problems of image registration and reconstruction was proposed. The CNN consists of two separate modules that are jointly trained by directly using pairs of unregistered images.
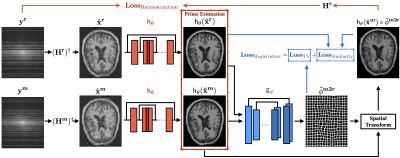
U-Dream jointly trains image reconstruction and image registration modules. Inputs are unregistered measurement pairs from the same subject. The zero-filled images are passed through the reconstruction CNN to remove artifacts due to noise and undersampling. The output images are then used in the registration CNN to obtain the motion field characterizing the directional mapping between their coordinates. We register one of the reconstructed images to the other by the Spatial Transform Network.
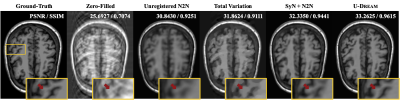
Illustration of several reconstruction methods on synthetic undersampled brain MRI images. The top-right corner of each image provides the PSNR and SSIM values with respect to the groundtruth image. Unregistered N2N is directly trained on unregistered data, while SyN+N2N trains the CNN on pre-registered images that are corrupted with artifacts. U-Dream achieves a significant improvement relative to both methods by jointly addressing the reconstruction and the registration problems.