Gaurav Verma1, Rebecca Emily Feldman2, and Priti Balchandani1
1Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, Canada
1Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC, Canada
An
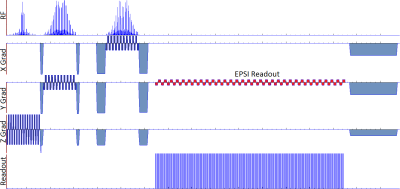
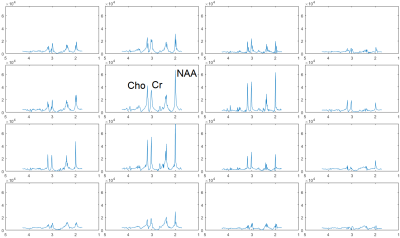
echo-planar spectroscopic imaging (EPSI) sequence has been demonstrated combining semi-adiabatic spatial-spectral pulses and echo-planar readout to facilitate fast magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) at ultra-high field (7T)