Junye Yao1, Zihan Zhou1, Benjamin C. Tendler2, Karla L. Miller2, Lei Zhang3, Keqing Zhu3, Aimin Bao3, Hongjian He1, and Jianhui Zhong1,4
1Center for Brain Imaging Science and Technology, College of Biomedical Engineering and Instrumental, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, FMRIB, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, London, United Kingdom, 3National Human Brain Bank for Health and Disease, School of Brain Science and Brain Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 4Department of Imaging Sciences, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, United States
1Center for Brain Imaging Science and Technology, College of Biomedical Engineering and Instrumental, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, FMRIB, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, London, United Kingdom, 3National Human Brain Bank for Health and Disease, School of Brain Science and Brain Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 4Department of Imaging Sciences, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, United States
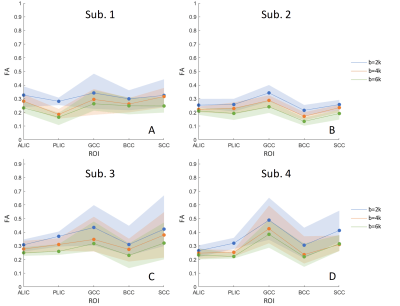
Dependence of FA on
b-value was investigated in 4 fixed human brain hemispheres. Analysis of noise effects
and an observed positive correlation between differences in FA across b-values
and mean kurtosis indicates that non-gaussian diffusion is a likely contributor to the
b-value dependence.
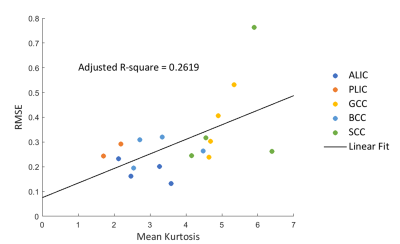
Figure
4 Linear correlation plots between RMSE (ordinate) and MK (abscissa). Different
colors represent different ROIs, all of the four subjects were plotted on the
same figure. RMSEs are calculated from discrepancy between FA derived from high
(b=6000 s/mm2) and low (b=4000 s/mm2) b-value datasets.
PLIC of subject 1 and subject 4 was excluded in this analysis due to their
insufficient SNR.