Michael Paquette1, Cornelius Eichner1, Guillermo Gallardo1, and Alfred Anwander1
1Neuropsychology, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany
1Neuropsychology, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany
We evaluate common heuristics to quantify axon diameters from axon shapes within a collection of EM images, using Monte-Carlo diffusion simulations. Further, we propose a simple heuristic optimised to better match the way dMRI sees axon shapes.
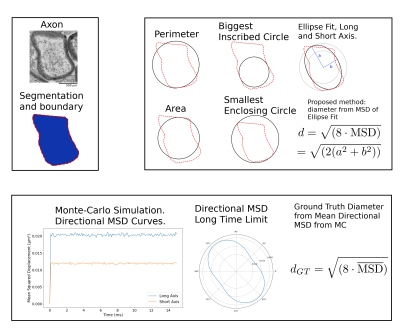
Figure 2: We isolate the segmentation mask of the intra-axonal volume. The pixel centers are used to compute a concave hull6 and extract a boundary. The boundary is used to compute the heuristic diameters: perimeter, area, biggest inscribed-circle, smallest enclosing-circle and ellipse fit. The mask is used as a boundary for a MC simulation of diffusion. The MC trajectories are used to compute the directional MSD of the shape, which is converted to a ground-truth diffusion-specific diameter.
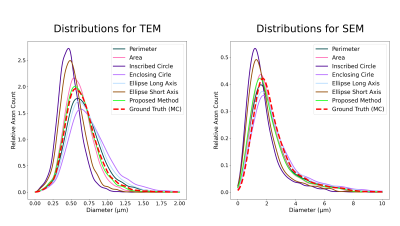
Figure 3: Axon diameter count distribution for all heuristics and MC based ground-truth. The densities were generated with a gaussian kernel density estimator. The proposed method approximates very accurately the ground-truth distribution in the case of high resolution TEM data. For the SEM data, all the distributions are close, except for the heavily underestimating method of inscribed-circle and ellipse short-axis.
