Davood Karimi1, Onur Afacan1, Clemente Velasco-Annis1, Camilo Jaimes1, Caitlin Rollins1, Simon Warfield1, and Ali Gholipour1
1Boston Children's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
1Boston Children's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
We propose a novel deep learning method for accurate and roust estimation of color fractional anisotropy from fetal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scans. The proposed method is significantly more accurate than standard estimation methods.
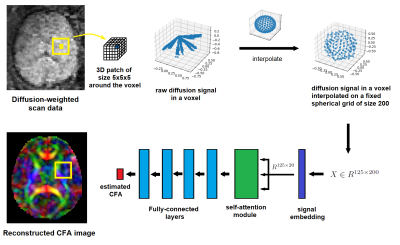
To estimate CFA in a voxel, a 3D patch of size 5 around that voxel is considered. The diffusion signal in each voxel is interpolated onto a fixed spherical grid of size 200. This results in a matrix of interpolated signals, X, where each of 125 rows is the signal for one of the voxels in the patch. The signals are first embedded into a smaller space of dimension equal to 20, where a self-attention module learns the correlation between the signals from neighboring voxels. A series of fully-connected layers are then applied to estimate the CFA for the voxel.
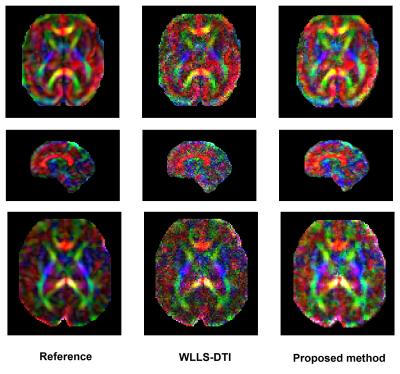
Comparison of our proposed method and WLLS-DTI on three fetal scans. In each row, the left image is the reference CFA image reconstructed with WLLS-DTI using the full DW-MRI measurements. The middle image is the CFA image reconstructed with WLLS-DTI using 20% of the measurements. The right image is the CFA image reconstructed with the proposed deep learning method using 20% of the measurements.