Yanqiao Ren1, Jingjie Yan2, Lian Yang1, Qingjia Bao3, Chaoyang Liu3, and Chuansheng Zheng1
1Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China, Wuhan, China, 2Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China., Wuhan, China, 3State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathmatics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, 430071Wuhan, China, Wuhan, China
1Department of Radiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China, Wuhan, China, 2Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China., Wuhan, China, 3State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathmatics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, 430071Wuhan, China, Wuhan, China
Correlation of functional MRI
with changes in tumor microenvironment following sorafenib and immunotherapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma
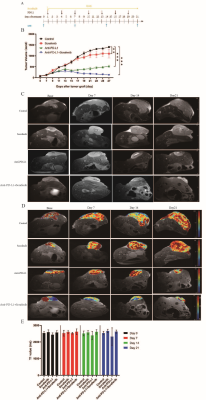
Combined administration of anti-PD-L1 antibody and sorafenib shows enhanced anti-tumor
effects. A: Flow chart of in vivo experiments. B: Response of the subcutaneous tumors to the indicated treatments. C: T2WI of four groups of
subcutaneous tumors before and at different time points after treatment. D: Pseudocolour
images (T1 mapping) of four groups of subcutaneous tumors before and at
different time points after treatment. E: T1 values of four groups of
subcutaneous tumors before and at different time points after treatment (P>0.05). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p<0.001.
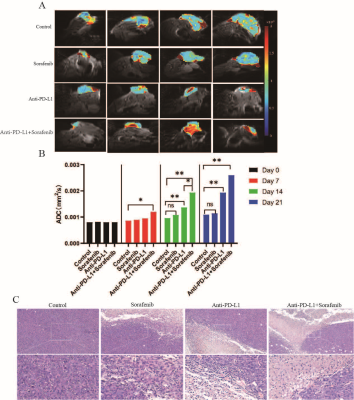
Water ADC maps of representative treated groups
obtained before therapy and at different times post-therapy. A, B: After 7 days
of treatment, the ADC value of the combined treatment group increased
significantly compared with the control group.C: Hematoxylin and eosin
(H&E)-stained histologic sections of representative treated groups obtained
at 21d post-therapy. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p<0.001.