Zheng Ye1, Bin Song1, Yuming Li1, Qing Li2, Lisha Nie3, and Xiaocheng Wei3
1West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2MR collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China, 3MR Research, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
1West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2MR collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China, 3MR Research, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Regardless
of breathing schemes, the measurements of liver ADC by using SMS-DWI showed
good reproducibility across different MR vendors. However, the measurements were
less reproducible between different breathing schemes, with breath-hold
technique showing more variations.
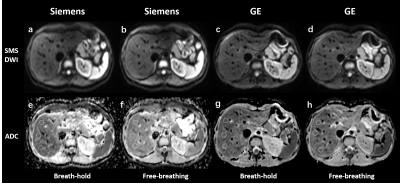
Figure 2. Simultaneous multi-slice
diffusion‑weighted images (SMS-DWI) and the corresponding apparent diffusion
coefficient (ADC) maps from two
breathing
schemes and
two vendors in a
volunteer. The upper row illustrates
SMS-DWI
(a-d) with b value of 50 s/mm2.
The lower row shows
ADC
maps (e-h), which were automatically generated on the MR system's console.
Three circle
region of interest (ROIs) in
the right liver lobe were firstly draw on SMS-DWI, and pasted to corresponding
ADC maps.
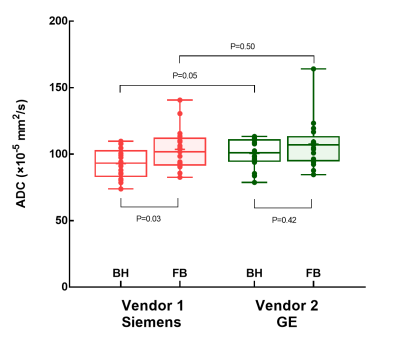
Figure 4. Box
and whisker plots illustrates the apparent
diffusion coefficient (ADC) measured
in the right liver lobe from two
breathing
schemes
and two vendors. In
vendor
1 (Siemens system), the
liver ADC of free-breathing SMS-DWI was significantly higher than that of
breath-hold SMS-DWI (P=0.03). In vendor
2 (GE system), no
significant difference was found in ADC
values from
different breathing schemes (P=0.42). The liver ADC values from two vendors did not show significant
difference in both breathing schemes (P=0.05 and P=0.50). BH, breath-hold; FB,
free-breathing.
