Neta Stern1, Dvir Radunsky1, Tamar Blumenfeld-Katzir1, Yigal Chechik2,3, Chen Solomon1, and Noam Ben-Eliezer1,4,5
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2Department of Orthopedics, Shamir Medical Center, Zerifin, Israel, 3Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 4Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 5Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research (CAI2R), New-York University, Langone Medical Center, NY, United States
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2Department of Orthopedics, Shamir Medical Center, Zerifin, Israel, 3Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 4Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 5Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research (CAI2R), New-York University, Langone Medical Center, NY, United States
The Marchenko-Pastur Principle Component Analysis denoising
algorithm can be used to improve the high-resolution mapping of quantitative T2
values. The technique was validated on in
vivo brain and knee data, leading to an increase in T2 maps
precision while preserving anatomical features.
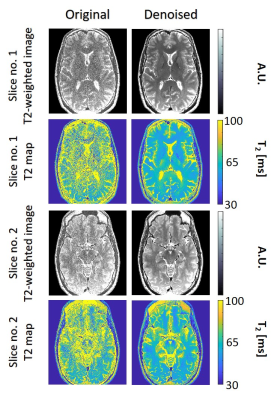
Figure
3: T2 weighted images and T2 maps for two slices acquired using the second high-resolution in vivo brain scan. Left / right columns show the pre- / post-denoising images and T2-maps (window size 15x15).
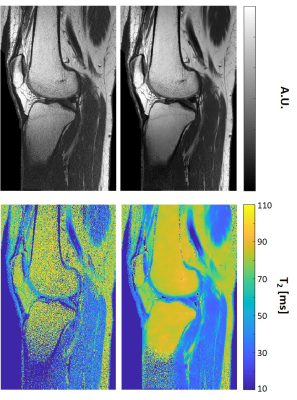
Figure
4: T2 weighted images and T2 maps of a selected slice acquired
using a high resolution in vivo knee scan (matrix size=448x280, FOV=192x120 mm2).
The left column shows the original images and T2-maps,
and the right column shows the corresponding images and T2 maps after MP-PCA image denoising
(window size 20x10).