Johnathan Le1,2, Jason Mendes2, Mark Ibrahim3, Brent Wilson3, Edward DiBella1,2, and Ganesh Adluru1,2
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 2Utah Center for Advanced Imaging Research, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 3Department of Cardiology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 2Utah Center for Advanced Imaging Research, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 3Department of Cardiology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States
By using an attention-gated multi-layer perceptron, T1 mapping sequences can potentially be accelerated by reducing the number of T1-weighted images required to produce high-quality T1 maps.
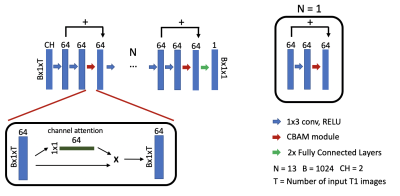
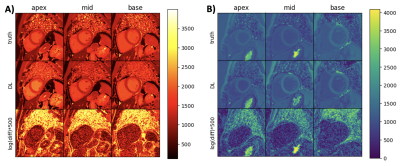
Figure 1. Illustration of the proposed attention-gated neural network for cardiac T1 mapping. Inputs to the network have dimensions of B x CH x 1 x T. CH = 2 corresponds to T1 weighted values and their inversion times. T corresponds to the number of input T1 images and inversion times for pre-contrast (T = 5) and post-contrast (T = 4) acquisitions. B = 1024 is the batch size. Scanner generated T1 maps were used as the reference.