Zhuopin Sun1, Steven Meikle2,3, and Fernando Calamante1,3,4
1School of Biomedical Engineering, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 3Brain and Mind Centre, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 4Sydney Imaging, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
1School of Biomedical Engineering, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 3Brain and Mind Centre, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 4Sydney Imaging, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
The proposed CONNectome-based Non-Local Means (CONN-NLM) exploits synergies between diffusion MRI-derived structural connectivity and PET intensity to denoise PET data. CONN-NLM can improve the overall PET image quality in gray matter and to enhance lesion contrast-to-noise ratio.
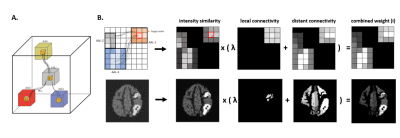
Fig. 2. A) Illustration of proposed connectome-based NLM
filter. The filtered value for any given voxel is computed by a weighted value
for every brain voxel. This weighting is based on voxel-wise PET intensity
similarity3
and connectivity strengths between each pair of parcellations (coloured cubes).
B) Top: schematic demonstration of computation of intensity similarity
matrix, distant and local connectivities. These 3 matrices are combed to form
the total weight. Bottom: a realistic example.
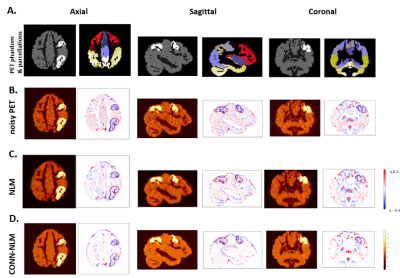
Fig. 3. A) Ground-truth simulated PET phantom and AAL
parcellations10.
B-D) Left: PET image; right: intensity difference relative to ground-truth,
calculated based on grey matter only. B) Reconstructed PET image with
noise. C) Smoothing performed by non-local means filter without
connectivity information.11
D) Smoothing performed by the proposed CONN-NLM filter.